L7 | CHATS
product feature
The L7|ESP™ Plasmid Editor Streamlines Plasmid Information Management Across a Unified Platform
by Oana I. Lungu | posted on April 02, 2024
Plasmids are a critical tool in molecular biology
Scientists have taken advantage of plasmids to clone, transfer, and manipulate genes for decades. By inserting any DNA fragment or gene of interest, scientists can create recombinant plasmids. Applications include protein engineering, gene editing, and high-throughput screening of genes or genetic elements. Plasmids contain rich information and complex structures, including multiple cloning sites, resistance genes, promoters, and other functional elements. This information is collected, organized, and stored throughout the laboratory and is used to drive key decisions. Capturing plasmid information in a way that enables easy access, editing, and annotation within interconnected laboratory systems can be challenging but is critical in realizing the value of rich plasmid data in a seamless, unified manner.
Maintaining plasmid information in laboratories poses challenges
In all situations, it is critical to collect, organize, and keep track of the plasmid information. Challenges in organizing this information in the laboratory include:
- Ensuring complex plasmid information is presented in an easily searchable, accessible, and viewable manner for comprehensive browsing.
- Providing effective mechanisms for versioning plasmids as they are evolved or modified so that users can access both original and modified versions.
- Integrating plasmid metadata with experiment information from the systems that capture it, such as ELN, for seamless retrieval and annotation across the laboratory.
L7|ESP Plasmid Editor applies FAIR data principles to easily access plasmid information
The Plasmid Editor has been integrated into the L7|ESP Unified Platform to allow for plasmid information usage in a FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) manner, ensuring ease of searchability, accessibility, and viewing. Using the Open Source Vector Editor Component (1), L7|ESP’s Plasmid Editor tool encompasses an advanced suite of functionalities that are highly sought after in vector mapping and sequence editing software, including:
- Allows plasmid information to be easily findable and accessible within a unified platform through the application of FAIR data principles.
- Enables viewing, editing, and annotation of plasmids in various formats (e.g., FASTA file format or GenBank format)
- Provides custom views of plasmid information, which supports easy filtering, browsing, and querying of data.
- Includes viewing of plasmid features such as gene details, cut sites, open reading frames, and translation information.
- Offers the ability to perform simulated digestions and simulated PCR reactions.
- Includes robust primer design tools for critical parameters such as melting temperatures and GC content
L7|ESP Plasmid Editor is part of the L7 Notebooks App. Download the datasheet to learn more.
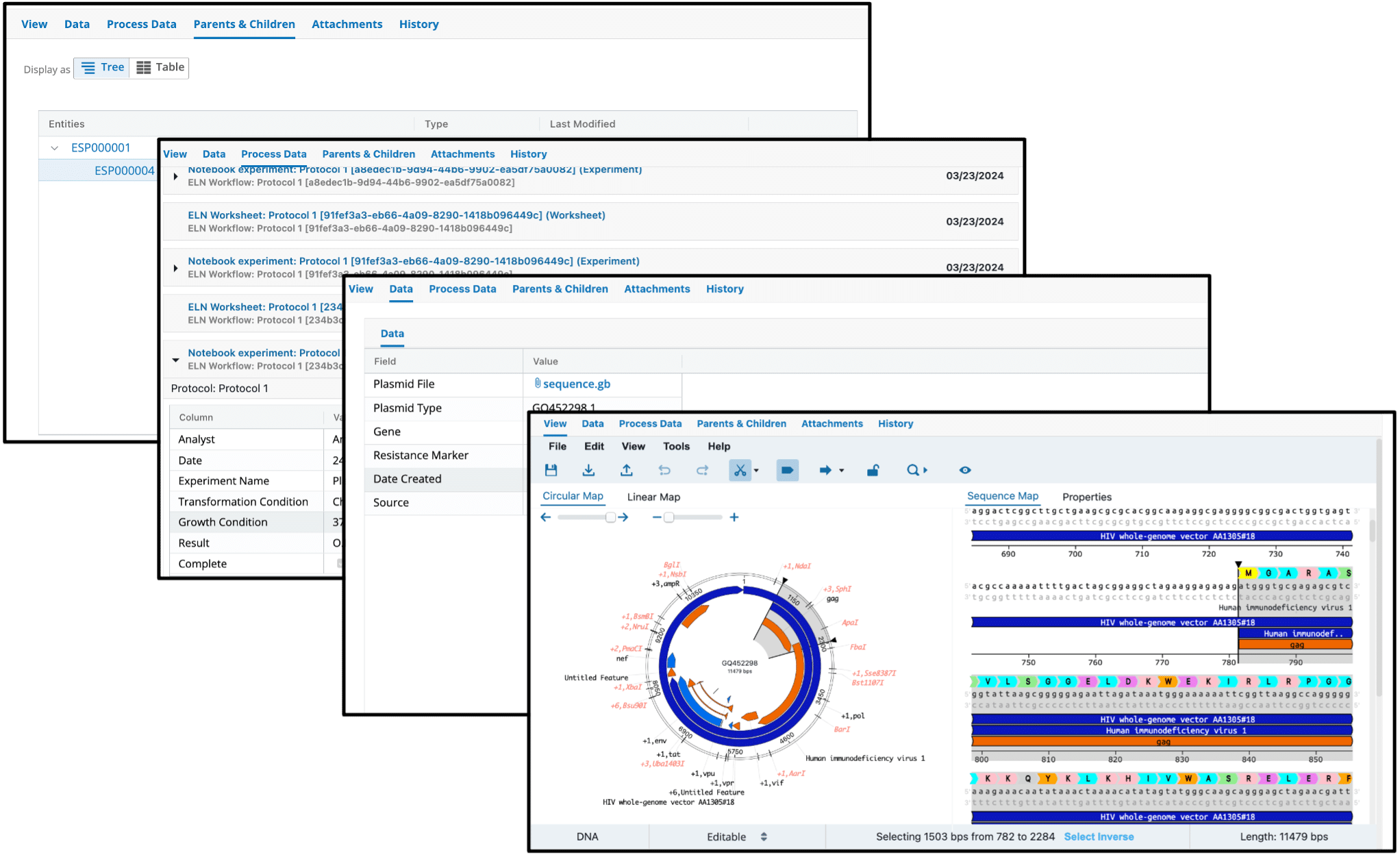
Figure 1: The Plasmid Editor within L7|ESP establishes relationships between plasmid versions, their metadata, experimental process data, and version features and edits.
The fully integrated L7|ESP Plasmid Editor leverages data relationships for plasmid versioning
By being fully integrated, the Plasmid Editor leverages the L7|ESP system to establish relationships for interconnected plasmid data. Users can edit plasmids, manage all the resulting metadata, and process information by creating parent-child relationships between the original and modified plasmids, enabling versioning as well as traceability of plasmids. Figure 1 depicts how L7|ESP provides data contextualization for plasmid information by managing all plasmid metadata, process information, and intricate relationships in one single source of truth as plasmids are versioned. Parent-child relationships are established as plasmids are edited to create new versions (Top Left). Information is linked to the appropriate version when it is captured in experiments as process data (Second to the Left). Plasmid metadata is also appropriately linked to the plasmid version (Second to the Right). Lastly, the plasmid custom view enables browsing of the versioned plasmid edits and features (Bottom Right).
L7|ESP utilizes the power of a platform to seamlessly integrate plasmid metadata with experiment information
Plasmid information is seamlessly connected across the L7|ESP unified platform with workflow orchestration. A built-in widget connects in L7|ESP’s Notebooks application to plasmid metadata information, allowing for unification of plasmid information directly from the moment of capture. Figure 2 depicts how users are able to create Notebook templates and associated entries to record a variety of experimental processes and their resulting information, such as instrument or protocol data, alongside viewing, editing, and annotation of plasmids. As experiment information about processes being performed using plasmids is captured in Notebook entries, the data are seamlessly synched to plasmid metadata, ensuring a holistic view of plasmid sequences, their annotations, and the experimental processes with which they have been associated.
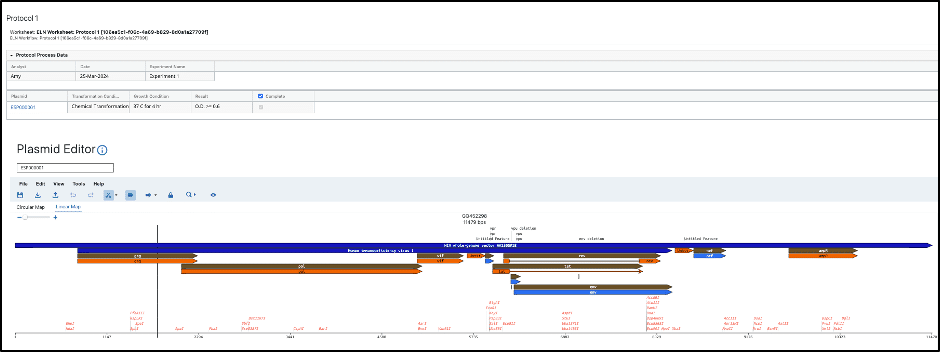
Figure 2. Notebook Entries allow for the consolidation of experimental process information with plasmid information seamlessly as the data is captured.
Think Biosciences uses the Plasmid Editor to evolve their plasmid library for new natural product screening.
Maintaining plasmid libraries can add an additional layer of complexity to laboratory processes, necessitating sifting through vast libraries of sequences and ensuring accurate data is tied to the correct variants. Access to the right tools enables streamlining of these procedures. The recently published Think Bioscience case study demonstrates the value of the integrated Plasmid Editor within the L7|ESP platform. For Think Bioscience, the plasmid is the pivotal component in their laboratory workflows and, as such, plays a critical role in their evolving internal R&D Standard Operating Procedure (SOP). Having the Plasmid Editor fully integrated into L7|ESP, with its Workflow Orchestration system, brings organization and efficiency to Think Bioscience’s R&D SOP implementation process. By streamlining library screening and data generation in one platform, the L7|ESP platform facilitates tracking, sorting, and storing all information in one single source of truth for Think Bioscience.
The Plasmid Editor, as integrated into the L7|ESP Platform, offers key functionality for tackling the challenges of capturing plasmid sequence information in a way that enables easy access, editing, and annotation within interconnected laboratory systems.
